Isometric shoulder exercises involve contracting muscles without joint movement, improving strength, stability, and endurance while minimizing injury risk, making them ideal for rehabilitation and overall fitness;
1.1 What Are Isometric Shoulder Exercises?
Isometric shoulder exercises are static holds that strengthen the shoulder muscles without joint movement. They involve contracting the muscles while maintaining a fixed position, often using resistance from walls, bands, or body weight. These exercises improve strength, stability, and endurance, making them ideal for rehabilitation, injury prevention, and enhancing overall shoulder function. They are simple, effective, and require minimal equipment.
1.2 Importance of Shoulder Strength for Overall Fitness
2.1 Improved Strength Without Joint Movement
Isometric shoulder exercises enhance muscle strength by holding static positions, engaging the muscles without moving the joints. This method is ideal for improving stability and power, especially for those with mobility limitations. By focusing on sustained contractions, isometric exercises effectively target the shoulder muscles, promoting strength gains while minimizing joint stress, making them beneficial for rehabilitation and overall fitness goals.

Benefits of Isometric Shoulder Exercises
Isometric shoulder exercises improve strength, enhance endurance, and boost stability. They reduce injury risk and aid in rehabilitation, making them versatile for fitness and recovery.
Isometric shoulder exercises enhance muscle strength by engaging the shoulders statically, eliminating joint movement. This method is effective for rehabilitation, as it avoids stress on injured joints while building resilience. Studies show improved muscle activation and stability, making it ideal for those recovering from injuries or seeking low-impact strength training. This approach promotes muscle endurance and overall shoulder health effectively.
2.2 Enhanced Muscle Endurance and Stability
Isometric shoulder exercises boost muscle endurance by holding static positions, challenging the muscles to sustain contractions. This improves stability, crucial for preventing injuries and enhancing athletic performance. The exercises target shoulder stabilizers, strengthening the rotator cuff and scapular muscles. Regular practice leads to better posture, reduced fatigue, and enhanced overall shoulder function, making daily activities and sports more efficient and injury-free.

2.3 Reduced Risk of Injury and Rehabilitation
Isometric shoulder exercises are excellent for injury prevention and rehabilitation as they strengthen muscles without joint stress, reducing strain on vulnerable areas. They help restore stability after injuries, improving joint integrity and lowering the risk of re-injury. These exercises are particularly beneficial for conditions like frozen shoulder or rotator cuff issues, offering a safe and effective way to rebuild strength and promote recovery.

Best Isometric Shoulder Exercises
Isometric shoulder exercises include wall presses, resistance band holds, and shoulder blade squeezes, offering effective ways to build strength and stability without joint movement or strain.
3.1 Wall Press for Shoulder Flexion
Stand facing a wall with your elbow bent at 90 degrees, fist against the wall. Press your arm into the wall without moving your shoulder, holding 5-10 seconds. Repeat 3 sets. This exercise strengthens shoulder flexion, improving posture and reducing injury risk, ideal for those with limited mobility or recovering from shoulder injuries.
3.2 Arm Against the Wall for External Rotation
Stand in a doorway with your arm against the wall, elbow bent at 90 degrees. Gently press the back of your hand into the wall to target external rotation; Hold for 5-10 seconds, repeating 3 sets. This exercise strengthens shoulder stability and improves joint function, ideal for rehabilitation and enhancing rotational strength without joint movement, reducing injury risk.
3.3 Resistance Band Isometric Holds
Stand holding a resistance band with arms at shoulder height. Pull the band gently, engaging your shoulders without moving your arms. Hold for 10-15 seconds, repeating 3 sets. This exercise targets shoulder muscles, improving strength and stability. It’s effective for enhancing endurance and preventing injuries, making it a versatile addition to any shoulder training routine.
3.4 Plank with Shoulder Blade Squeeze
Start in a plank position with hands under shoulders and toes on the ground. Engage your core, squeeze your shoulder blades together, and hold for 10-15 seconds. Repeat for 3 sets. This exercise strengthens shoulder stability, improves posture, and enhances overall core strength, making it a comprehensive addition to shoulder training routines.

Proper Form and Technique
Proper form and technique are crucial for maximizing the benefits of isometric shoulder exercises. Maintain correct posture, engage your core, and avoid unnecessary movement to ensure effective muscle activation and prevent injury.
4.1 Maintaining Posture and Alignment
Maintaining proper posture and alignment is essential during isometric shoulder exercises. Stand or sit upright with shoulders relaxed, engage your core, and ensure your spine is neutral. This prevents strain and ensures targeted muscle activation. Incorrect posture can lead to ineffective exercises or potential injury, emphasizing the need for awareness and control throughout each movement.
4.2 Avoiding Compensation from Other Joints
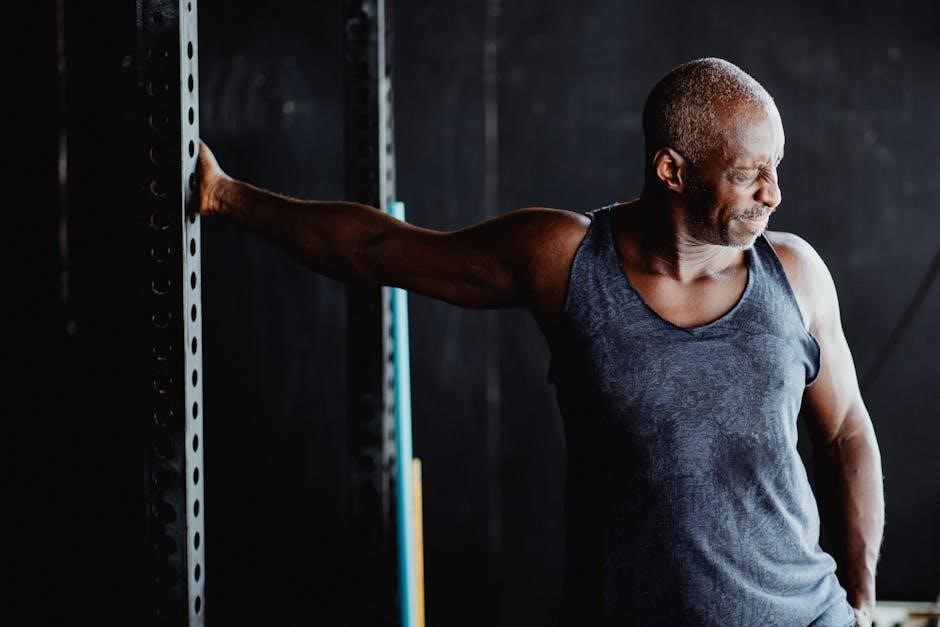

Avoiding compensation from other joints is critical during isometric shoulder exercises. Ensure that only your shoulders are engaging, preventing your neck, lower back, or other joints from assisting. Maintain proper form by keeping your core engaged and staying aware of your body positioning. This focus prevents ineffective movements and reduces the risk of injury, ensuring the shoulder muscles are effectively targeted and strengthened without unnecessary strain on other areas.
4.3 Using Breathing Techniques Effectively
Proper breathing is essential for maximizing the effectiveness of isometric shoulder exercises. Exhale slowly during the contraction phase to stabilize your core and maintain proper form. Inhale naturally as you release the hold. Avoid holding your breath, as this can increase tension and reduce focus. Consistent, controlled breathing helps maintain posture, prevents compensation, and ensures safe, effective execution of the exercises.
Safety Considerations and Precautions
Consult a professional before starting isometric shoulder exercises, especially if you have injuries. Gradually increase intensity to avoid overstrain. Avoid any movements causing pain or discomfort.
5.1 Consulting a Professional Before Starting
It’s crucial to consult a physical therapist or trainer before beginning isometric shoulder exercises, especially if you have existing injuries or discomfort. They can tailor exercises to your needs, ensuring safety and effectiveness. Professional guidance helps prevent overexertion and improper form, which can lead to further injury or slow recovery. This step is essential for maximizing benefits while minimizing risks.
5.2 Gradually Increasing Intensity
Start with low-intensity isometric holds, gradually increasing duration and resistance as strength improves. For example, begin with 5-second holds and progress to 30 seconds. Use pillows or resistance bands to add challenge. Avoid sudden jumps in intensity to prevent strain. Consistent, patient progression ensures sustainable gains and reduces injury risk, allowing shoulders to adapt and strengthen effectively over time.
5.3 Avoiding Pain or Discomfort
Prioritize comfort and stop immediately if pain occurs. Monitor discomfort levels during exercises and adjust techniques or intensity as needed. Avoid pushing through pain to prevent injury. If discomfort persists, consult a professional to modify the routine. Proper form and gradual progression are key to safe and effective isometric shoulder training, ensuring long-term benefits without compromising joint health.
Incorporating Isometric Shoulder Exercises into Your Workout Routine
Incorporate isometric shoulder exercises 2-3 times weekly, holding each for 5-10 breaths. Combine with dynamic movements for balanced strength. Track progress and adjust as needed.
6.1 Frequency and Duration of Sessions
Perform isometric shoulder exercises 2-3 times weekly, holding each position for 20-30 seconds. Start with 3 sets per session, gradually increasing duration as strength improves. Adjust frequency based on recovery and progress, ensuring adequate rest between sessions to avoid overtraining. Consistency is key for optimal results and muscle adaptation.
6.2 Combining with Other Training Methods
Combine isometric shoulder exercises with dynamic movements, like arm circles or resistance band exercises, to enhance strength and mobility. Incorporate techniques like planks or wall slides to target multiple muscle groups. Mixing isometric holds with functional training improves overall shoulder stability and reduces injury risk, creating a balanced and effective workout routine.
6.3 Tracking Progress and Adjustments
Track progress by recording hold duration, resistance levels, and muscle endurance improvements. Regularly assess strength gains and adjust intensity as needed. Use a workout log to monitor consistency and advancements. Gradually increase hold times or resistance to challenge muscles further, ensuring continuous improvement without overexertion. Adjustments should be based on individual progress and feedback, maintaining a balanced and effective routine.
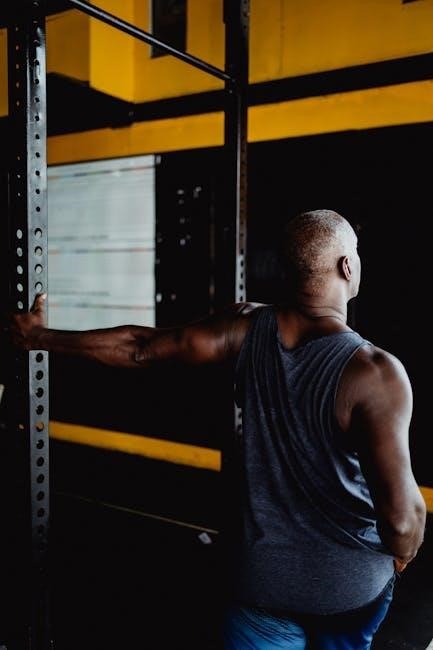

Isometric Shoulder Exercises PDF Guide
A comprehensive PDF guide offers detailed instructions, exercise descriptions, and safety tips for isometric shoulder workouts, helping users achieve strength and stability effectively at home.
7.1 Key Features of a Comprehensive PDF Guide
A comprehensive PDF guide on isometric shoulder exercises typically includes detailed instructions, exercise descriptions, safety tips, and progress tracking. It often features visual aids like diagrams and photos to demonstrate proper form and techniques. Many guides also offer customizable workout plans, addressing various fitness levels and goals. Some include video links or QR codes for further instruction, ensuring users can perform exercises safely and effectively to maximize results.
7.2 Where to Find Reliable Resources
Reliable resources for isometric shoulder exercises can be found on reputable websites like OrthoIndy and VCH, offering detailed PDF guides. Many orthopedic and physical therapy websites provide free downloadable materials. Search terms like “isometric shoulder exercises PDF” or “shoulder strengthening guide” yield comprehensive resources. Ensure the source is credible, such as medical or fitness professionals, to guarantee safe and effective workout plans.

Real-Life Success Stories and Testimonials
- Athletes report improved shoulder strength and endurance after incorporating isometric exercises into their routines, enhancing performance and reducing injury risks.
- Individuals with shoulder injuries share testimonials of successful rehabilitation using isometric exercises, highlighting pain reduction and faster recovery times.
- Many fitness enthusiasts praise isometric shoulder exercises for their effectiveness in building stability and overall shoulder health without requiring heavy equipment.
8.1 Athletes and Fitness Enthusiasts Sharing Experiences
- Athletes and fitness enthusiasts highlight the effectiveness of isometric shoulder exercises in improving performance and reducing injury risks.
- Many share testimonials of enhanced shoulder stability and strength, enabling better endurance during intense workouts and sports activities;
- Individuals recovering from shoulder injuries praise these exercises for their role in rehabilitation, often avoiding surgery and restoring mobility.
- Fitness enthusiasts appreciate the convenience of isometric exercises, requiring minimal equipment while delivering significant results for shoulder health.
- Overall, these experiences underscore the versatility and benefits of isometric shoulder exercises for both athletes and general fitness seekers.
8.2 Case Studies of Injury Rehabilitation
Case studies demonstrate the efficacy of isometric shoulder exercises in rehabilitation, particularly for injuries like frozen shoulder or rotator cuff strains.
- Individuals with frozen shoulder reported improved range of motion and reduced pain after consistent isometric practice.
- Post-surgery patients used isometric holds to regain strength without risking further injury.
- These exercises are often prescribed for gradual, safe recovery, emphasizing controlled muscle engagement.
- Studies highlight their role in preventing re-injury and restoring functional shoulder movement.
Isometric shoulder exercises are a valuable tool for improving strength, stability, and rehabilitation, offering effective results with minimal risk of injury or strain.
9.1 Summary of the Importance of Isometric Shoulder Exercises
Isometric shoulder exercises are essential for building strength, stability, and endurance without joint movement, making them ideal for rehabilitation, injury prevention, and enhancing overall fitness. They are low-impact, accessible, and effective for individuals of all fitness levels, promoting shoulder health and functionality in daily activities and sports performance.
9.2 Encouragement to Start Implementing the Exercises
Embrace isometric shoulder exercises as a simple yet powerful way to enhance your fitness journey. These exercises are accessible to everyone, requiring minimal equipment and offering significant benefits for strength, stability, and posture. By incorporating them into your routine, you’ll notice improved shoulder function and reduced injury risk. Start today and take the first step toward stronger, healthier shoulders with the guidance of a reliable PDF resource.
