This comprehensive guide covers key biological concepts‚ including cell structure‚ genetics‚ evolution‚ and ecology. It provides effective study strategies‚ such as active learning and flashcard use‚ to help students prepare confidently for their final exam.

Welcome to the Biology Final Exam Study Guide‚ designed to help you navigate and master the essential concepts covered throughout the semester. This guide is structured to provide a clear roadmap for effective preparation‚ ensuring you feel confident and ready for your exam.
Within these pages‚ you will find a detailed overview of key biological principles‚ including cell structure‚ genetics‚ evolution‚ and ecology. Each section is tailored to address common exam topics‚ offering practical strategies for active learning‚ time management‚ and stress reduction. Whether you are reviewing complex processes like photosynthesis or brushing up on Mendelian genetics‚ this guide equips you with the tools to succeed.
By focusing on interactive study methods‚ such as flashcards‚ practice exams‚ and group discussions‚ this guide encourages a holistic approach to learning. It also emphasizes the importance of maintaining physical and mental well-being during exam preparation. Use this resource to identify your strengths and weaknesses‚ and approach your final exam with clarity and confidence.

Key Biological Concepts and Processes
Mastering key biological concepts is fundamental to excelling in your final exam; This section focuses on the core principles that form the foundation of biology‚ including cell structure‚ genetics‚ evolutionary biology‚ and ecology. Understanding these concepts will help you tackle complex questions and apply your knowledge effectively.
Cell structure and function are essential‚ as cells are the basic units of life. Genetics‚ both Mendelian and molecular‚ explores inheritance patterns and DNA processes. Evolutionary biology explains how species adapt and change over time‚ while ecology examines interactions within ecosystems. These topics are interconnected and often appear in exam questions.
By studying these areas thoroughly‚ you will gain a comprehensive understanding of biological systems. Use flashcards and practice exams to reinforce your knowledge‚ and attend review sessions to clarify doubts. This section serves as a roadmap to guide your studying and ensure you are well-prepared for the exam.
2.1 Cell Structure and Function
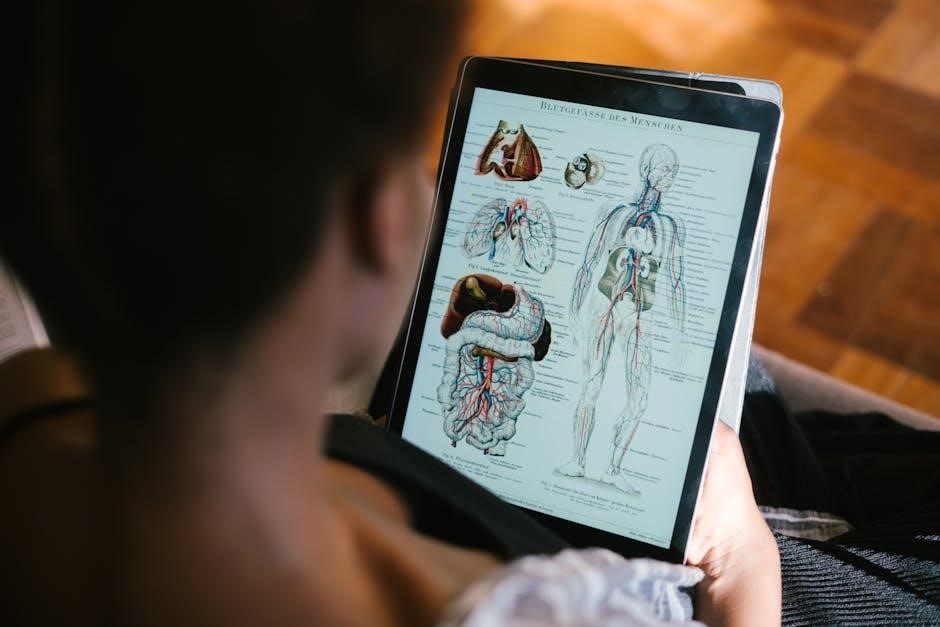
Understanding cell structure and function is critical for success in biology. Cells are the basic structural and functional units of life‚ and their components play vital roles in maintaining cellular activity. Key concepts include the differences between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells‚ organelle functions‚ and the cell membrane’s role in transport.
- Cell Membrane: Controls the movement of materials in and out of the cell through active transport‚ passive transport‚ and osmosis.
- Organelles: Such as the nucleus (DNA storage)‚ mitochondria (energy production)‚ and ribosomes (protein synthesis) are essential for cellular processes.
- Cell Division: Processes like mitosis and meiosis are fundamental for growth‚ repair‚ and reproduction.
Focus on understanding how these components interact to maintain cellular homeostasis. Practice identifying organelles and their functions‚ and review processes like photosynthesis and cellular respiration. These topics are often emphasized in final exams‚ so thorough preparation is essential for achieving a high score.

2.2 Genetics: Mendelian and Molecular Genetics

Genetics is a cornerstone of biology‚ focusing on heredity and the variation of organisms. Mendelian genetics‚ established by Gregor Mendel‚ explores how traits are inherited through laws such as segregation and independent assortment. These principles explain how genes are passed from one generation to the next.
- Mendelian Genetics: Key concepts include dominant and recessive traits‚ Punnett squares for predicting offspring traits‚ and the statistical nature of genetic inheritance.
- Molecular Genetics: Delve into DNA structure‚ replication‚ and gene expression. Understand transcription‚ translation‚ and how genes code for proteins.
Focus on understanding mutations‚ genetic variation‚ and modern techniques like CRISPR. Review how environmental factors influence gene expression and the role of nucleic acids in genetic processes. These topics are pivotal for mastering genetics in your biology exam.
2.3 Evolutionary Biology and Natural Selection
Evolutionary biology examines how species change over time through natural selection and genetic variation. Key concepts include Darwin’s theory of evolution by natural selection‚ where organisms with favorable traits are more likely to survive and reproduce. Understand speciation‚ the formation of new species‚ and how it arises from reproductive isolation.

- Natural Selection: Learn how environmental pressures drive adaptation‚ leading to the survival of fittest individuals.
- Mechanisms of Evolution: Study genetic drift‚ gene flow‚ mutation‚ and non-random mating as drivers of evolutionary change.
- Evidence for Evolution: Review fossil records‚ comparative anatomy‚ molecular biology‚ and biogeography to understand evolutionary relationships.
Focus on key terms like “descent with modification” and “adaptive radiation.” Practice analyzing evolutionary trees and calculating evolutionary rates. These concepts are essential for grasping the dynamics of life’s diversity and change over time.
2.4 Ecology and Ecosystem Dynamics
Ecology and ecosystem dynamics focus on the interactions between organisms and their environment. Understand energy flow through ecosystems‚ starting with producers (autotrophs) and moving to consumers (heterotrophs). Key concepts include food webs‚ trophic levels‚ and the importance of decomposers in nutrient cycling.
- Biogeochemical Cycles: Study the carbon‚ nitrogen‚ and water cycles‚ which sustain life by recycling nutrients.
- Ecosystem Services: Recognize the role of ecosystems in providing oxygen‚ clean water‚ and soil formation.
- Community and Population Ecology: Learn about species interactions‚ predator-prey relationships‚ and the factors influencing population growth.
- Human Impact: Explore how human activities affect ecosystems‚ including deforestation‚ pollution‚ and climate change.
Focus on understanding how ecosystems maintain balance and respond to disturbances. Practice interpreting ecological pyramids and analyzing case studies of ecosystem disruption. These concepts are critical for comprehending the interconnectedness of life on Earth.
Effective Study Strategies
Mastering biology requires a structured and consistent approach to studying. Begin by organizing your notes and identifying key concepts from lectures and textbooks. Active learning techniques‚ such as summarizing information in your own words and teaching others‚ enhance retention. Use flashcards to memorize vocabulary and processes‚ focusing on terms like “autotroph‚” “ecosystem‚” and “photosynthesis.”
- Active Learning: Engage with material through discussions‚ problem-solving‚ and hands-on activities.
- Flashcards and Mnemonics: Simplify complex topics using visual aids and memory tricks.
- Practice Exams: Test your knowledge with past papers to identify weaknesses and improve time management.
- Study Groups: Collaborate with peers to review challenging topics and share insights.
Balance study sessions with short breaks to maintain focus and reduce burnout. Prioritize understanding over memorization‚ as this fosters deeper comprehension. Regular review and application of concepts will ensure long-term retention and confidence for the exam.
3.1 Active Learning Techniques
Active learning is a powerful approach to mastering biology‚ promoting deeper understanding and retention. Engage with course material by summarizing key concepts in your own words and teaching them to others. Participate in group discussions and debates to explore complex topics from different perspectives. Hands-on activities‚ such as lab experiments and simulations‚ reinforce theoretical knowledge and make learning interactive.
- Self-Quizzing: Test yourself regularly on concepts like cellular processes and ecological dynamics to identify gaps in understanding.
- Problem-Solving: Apply biological principles to real-world scenarios‚ enhancing critical thinking and analytical skills.
- Concept Mapping: Visualize relationships between topics‚ such as genetics and evolution‚ to build a cohesive knowledge framework.
By actively engaging with the material‚ you’ll develop a stronger grasp of biological concepts and improve your ability to apply them during exams.
3.2 Using Flashcards and Practice Exams
Flashcards and practice exams are essential tools for effective biology exam preparation. Flashcards help memorize key terms‚ processes‚ and concepts‚ such as cellular structures or genetic principles‚ by providing quick‚ focused reviews. Write the term on one side and the definition or explanation on the other‚ and quiz yourself frequently. Practice exams simulate real test conditions‚ allowing you to assess your knowledge under time pressure and identify areas needing improvement. Look for exams covering topics like ecology‚ evolution‚ and molecular biology to ensure comprehensive preparation.
- Use Flashcards Daily: Review a set of cards regularly‚ focusing on difficult topics like metabolic pathways or ecosystem dynamics.
- Take Timed Practice Exams: Mimic exam conditions to improve time management and reduce anxiety.
- Analyze Mistakes: After practice exams‚ review incorrect answers to understand and correct misunderstandings.
Combining flashcards with practice exams creates a well-rounded study routine‚ helping you feel confident and prepared for the final exam;
3.3 Group Study Methods
Group study methods are a powerful way to engage with biology material‚ fostering collaboration and deeper understanding. Working with peers allows you to discuss complex concepts‚ clarify doubts‚ and learn from one another’s strengths. Start by forming small groups of 3-4 students to ensure active participation. Assign roles‚ such as a leader to guide discussions and a recorder to summarize key points.

- Peer Teaching: Take turns explaining topics like cellular respiration or photosynthesis to reinforce your own knowledge.
- Problem-Solving Sessions: Tackle practice questions or past exams together‚ discussing each step thoroughly.
- Concept Mapping: Create visual diagrams of processes like ecosystems or genetic inheritance to visualize relationships.

Set clear agendas for each session to stay focused. Use shared resources like flashcards or study guides to align your efforts. Encourage open communication and constructive feedback to maximize learning. Balancing group work with individual study ensures a well-rounded preparation strategy for the final exam.
Managing Exam Anxiety
Exam anxiety is a common challenge‚ but there are effective ways to manage it. Start by acknowledging your feelings and reframing them as motivation. Practice relaxation techniques‚ such as deep breathing exercises or mindfulness meditation‚ to calm your mind. Establishing a consistent sleep routine and maintaining a healthy diet can significantly reduce stress levels. Regular physical activity‚ like walking or yoga‚ also helps alleviate tension and improves focus.
- Stay Organized: Create a detailed study schedule and stick to it to avoid last-minute cramming.
- Visualize Success: Imagine acing the exam to build confidence and reduce fear of failure.
- Seek Support: Talk to friends‚ family‚ or a counselor about your concerns to gain perspective and reassurance.
Remember‚ it’s normal to feel nervous‚ but by addressing anxiety proactively‚ you can approach the exam with clarity and confidence. Focus on what you can control and trust in your preparation. Stay positive and remind yourself that this exam is just one step toward your larger goals.
4.1 Time Management During Preparation
Effective time management is crucial for successful exam preparation. Start by creating a detailed study plan that outlines specific goals for each study session. Organize your notes and materials in advance to avoid wasting time searching for information. Break your study sessions into manageable intervals‚ such as 45-60 minutes of focused study followed by a 10-minute break‚ to maintain concentration and prevent burnout. Prioritize challenging topics and allocate more time to areas where you need improvement. Avoid cramming by spreading your study sessions evenly over several weeks. Set specific daily goals and track your progress to stay motivated. Incorporate practice exams or past papers to simulate exam conditions and identify weak areas. Remember to balance study time with rest and relaxation to maintain mental clarity. By adhering to a structured schedule‚ you can cover all necessary material without feeling overwhelmed.
4.2 Maintaining Physical and Mental Health
Maintaining physical and mental health is essential for optimal exam preparation. Ensure you get adequate sleep each night‚ as it improves memory retention and cognitive function. A balanced diet rich in fruits‚ vegetables‚ and whole grains provides the energy needed for focused study sessions. Stay hydrated by drinking plenty of water throughout the day; Regular exercise‚ such as walking or yoga‚ helps reduce stress and improve concentration. Mental health is equally important; practice mindfulness‚ meditation‚ or deep-breathing exercises to manage anxiety. Take regular breaks to avoid burnout and engage in activities that help you relax‚ such as reading or listening to music. Avoid excessive caffeine and sugary snacks‚ as they can lead to energy crashes. Connecting with friends or family can provide emotional support and help maintain a positive mindset. By prioritizing your well-being‚ you’ll be better equipped to tackle your studies and perform at your best during the exam.
